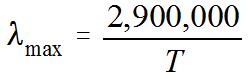
PHYSICS 1040 - ELEMENTARY ASTRONOMY - HOMEWORK #3
1. When white sunlight passes through a prism, it is broken into a rainbow-like _______________ spectrum. Joseph Fraunhofer discovered that the Sun's spectrum contains many dark _______________ lines. Each atom or molecule has its own pattern of characteristic spectral lines. By studying these lines, astronomers can determine which atoms and molecules are found on the Sun, planets, and other stars.
2. A hot dense object or gas gives off _______________ radiation. This consists of light of all colors (wavelengths), so when this light passes through a prism it produces a _______________ spectrum. Because a star is a ball of hot dense gas, it behaves like a _______________.
3. Suppose the temperature (in kelvins) of blackbody 1 is three times as great as that of blackbody 2. Then the energy released per second by each square meter of the surface of blackbody 1 is __________ times the energy released per second by each square meter of the surface of blackbody 2.
4. Wien's Law says that the peak wavelength of a blackbody spectrum is
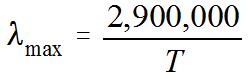
in units on nanometers (nm). (1 nm = 1 x 10-9 m.) So, if you are given the temperature T (in kelvins) of an object, you can find the wavelength at which most of the light is emitted.
a. For gas spiraling into a black hole, T = 1,000,000 K, so
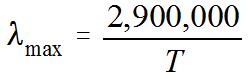 =
__________ nm.
=
__________ nm.
This is in the ______________ part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
b. For a star with surface temperature T = 25,000 K, so
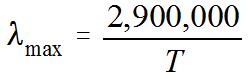 =
__________ nm.
=
__________ nm.
This is in the ______________ part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
c. For the Sun with surface temperature T = 5800 K, so
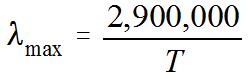 =
__________ nm.
=
__________ nm.
This is in the ______________ part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
d. For an interstellar cloud of gas, ices, and dust, T = 15 K, so
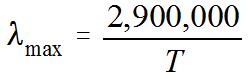 =
__________ nm.
=
__________ nm.
This is in the ______________ part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
e. For the universe as a whole, T = 2.7 K, so
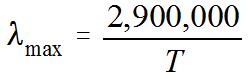 =
__________ nm.
=
__________ nm.
This is in the ______________ part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
5. The energy of a photon is E = h
v = hc/λ so, if photon 1 has twice the wavelength of photon 2, then the energy of photon 1 is _______________ the energy of photon 2.6. List the following from longest to shortest wavelength: blue light, gamma rays, infrared, radio waves, red light, ultraviolet, x-rays: _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________.
List the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum from smallest to largest photon energy: blue light, gamma rays, infrared, radio waves, red light, ultraviolet, x-rays:
_______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________.
7. An __________ is the smallest possible piece of a chemical element. It is made of three types of particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. The tiny central nucleus of the atom contains the massive __________ and __________. The less massive __________ orbit about the nucleus. The __________ force holds the negatively charged __________ in orbit around the positively charged nucleus. Each element has its own characteristic spectrum because the electron __________ levels (or orbits) are different for different elements. The energy of a __________ that is absorbed or emitted by an atom must be equal to the __________ in the energies of two of the atom= s __________ levels.
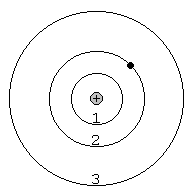
8. When a continuous spectrum is viewed through a cool gas, dark _______________ lines appear in the continuous spectrum. This occurs because atoms in the cool gas _______________ some of the photons at certain wavelengths from the continuous spectrum. In this case, electrons jump from lower/higher (circle one) to lower/higher (circle one) orbits in the atoms. The drawing at right shows an atom of hydrogen (one electron orbiting a single proton in the nucleus). Draw the electron and photon as the electron jumps from the second orbit to the third orbit when it absorbs the incoming photon. This particular process produces a dark absorption line in the spectrum of hydrogen at 656.3 nm, called the Hα absorption line.
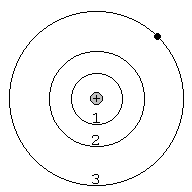
9. A hot, rarefied (less dense) gas produces bright _______________ lines. This occurs because atoms in the hot, rarefied gas _______________ photons at certain wavelengths. In this case, electrons fall from lower/higher (circle one) to lower/higher (circle one) orbits in the atoms. The drawing at right shows an atom of hydrogen. Draw the electron and photon as the electron falls from the third orbit down to the second orbit when it emits a photon. This particular process produces a bright emission line in the spectrum of hydrogen at 656.3 nm, called the Hα emission line.
10. The speed of a star toward or away from us can be found from the _______________ shift of its spectral lines. The light from a star moving toward us has its wavelength compressed (shortened), so its light looks more _______________. This is called a __________shift. The light from a star moving away from us has its wavelength stretched out (lengthened), so its light looks more _______________. This is called a __________shift.