Exam 1 Winter 2001 Version A
1. (4) What is the Milky Way in our sky, and how is it related to the Milky Way Galaxy?
2. (4) What does it mean when we say "angular size" of an object? Why can we
measure only angular sizes for objects in the sky?
3. (1) When traveling north into Canada, we see the North Star getting
A) brighter.
B) dimmer.
C) lower in the sky.
D) higher in the sky.
E) farther away.
4. (1) If you measure the angle between the horizon and Polaris to be 50 degrees,
you must be at
A) 50 degrees longitude. B) 40 degrees latitude.
C) 50 degrees latitude. D) 40 degrees longitude.
5. (1) If you were standing on Earth's equator, where would you look to see the
North Celestial Pole?
A) along the horizon. B) directly overhead. C) along the zodiac.
D) towards the ecliptic.
6. (1) If the Earth, still at 150 million kilometers from the Sun, took twice as
many days to orbit the Sun, the stars would appear to rise and set every
A) 12 hours. B) 6 hours. C) 48 hours.
D) 24 hours. E) 730 days.
7. (4) Where is the center of the Universe? (Fremont is not the right answer).
8. (4) There are 88 official constellations spread around the celestial sphere. If
you can see about 44 constellations at the North Pole over the course of a year,
about how many could you see from the equator? Explain your answer.
9. (1) The energy attributed to an object by virtue of its motion is known as
A) mass energy. B) potential energy.
C) kinetic energy. D) radiative energy.
10. (1) Scientists report the average kinetic energy of particles in a material
as the
A) temperature. B) ionization.
C) mass-energy equivalent. D) heat.
11. (1) Which of the following has the greatest kinetic energy?
A) the Space Shuttle gliding without engines at 300 mph
B) the Space Shuttle launching at 1,000 mph with rockets at full throttle
C) the Space Shuttle one hour before launch, perched 10 meters off the ground
D) the Space Shuttle orbiting at 17,000 mph with rockets off
12. (1) When space probe Voyager 2 passed by Saturn, it increased its speed.
Explain this from the point of view that Sir Isaac Newton would have.
13. (1) When a comet comes close to the Sun (the radius of its orbit decreases),
it must move faster because
A) of conservation of angular momentum
B) it is being pushed by the solar wind.
C) it "feels" a weaker gravitational pull
D) it is being pulled by the solar wind
14. (3) When a rock is held above the ground, we say it has some potential energy.
When we let it go, it falls and we say the potential energy is converted to kinetic
energy. Finally, the rock hits the ground. What has happened to the energy?
15. (1) An atom in an excited state contains more of what type of energy than the
same atom in the ground state?
A) gravitational potential energy
B) mass-energy
C) kinetic energy
D) thermal energy
E) electric potential energy
16. (1) How can an electron in an atom lose energy to go from a higher energy
level to a lower energy level?
A) It loses kinetic energy.
B) It absorbs a photon equal in energy to its own energy drop.
C) It releases a photon equal in energy to its own energy drop.
D) It exchanges gravitational potential energy for kinetic energy.
E) It loses gravitational potential energy.
17. (1) According to the universal law of gravitation, the force due to gravity is
A) directly proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
B) directly proportional to the distance between objects.
C) inversely proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
D) not dependent on the distance between objects.
E) inversely proportional to the distance between objects.
18. (1) According to the universal law of gravitation, if you increase the distance
between two objects by a factor of 10, then the gravitational force between them will
A) decrease by a factor of 10.
B) increase by a factor of 100.
C) decrease by a factor of 5.
D) increase by a factor of 10.
E) decrease by a factor of 100.
19. (1)According to the universal law of gravitation, if you triple the mass of only
one of the attracting objects, then the gravitational force between them will
A) not change at all.
B) decrease by a factor of 3.
C) decrease by a factor of 9.
D) increase by a factor of 3.
E) increase by a factor of 9.
20. (1)The frequency of a wave is
A) measured in hertz (Hz).
B) equal to the speed of the wave divided by the wavelength of the wave.
C) measured in cycles per second.
D) the number of peaks passing by any point each second.
E) All of the above.
21. (1)The wavelength of a wave is
A) the distance between where the wave is emitted and where it is absorbed.
B) the distance between a peak of the wave and the next trough.
C) how strong the wave is.
D) equal to the speed of the wave times the wave's frequency.
E) the distance between two adjacent peaks of the wave.
22. (1)We can see each other in the classroom right now because we
A) emit visible light.
B) emit infrared light.
C) emit thermal radiation.
D) reflect infrared light.
E) reflect visible light.
23. (1)Which of the following statements about thermal radiation is always true?
A) A hot object emits more radio waves than a cool object.
B) A hot object emits less total radiation than a cool object.
C) A hot object emits more X rays than a cool object.
D) A hot object emits more total radiation per unit surface area than a cool object.
**Following is a schematic of the energy levels of an atom. An electron has been
excited from energy level 1 to energy level 5 by absorbing a photon. (Questions 24-28)
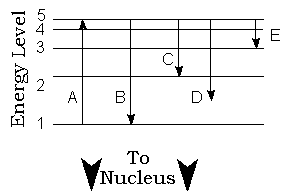
24. (2) Which transition to lower energies represents the smallest energy change? _____
25. (2) Which transition, as shown, is not possible? _____
26. (2) Which of the transitions resulting in emission represents the reddest
wavelength? _____
27. (2) Which of the transitions resulting in an emission line represents the
bluest wavelength? _____
28. (2) Which of the transitions resulting in an emission line results in a photon
with the same energy as that absorbed originally? _____
29. (1) The spectrum of argon gas looks like
A) helium, which is also an inert element
B) krypton, since it has similar chemical properties
C) ionized neon
D) no other element
E) none of the above
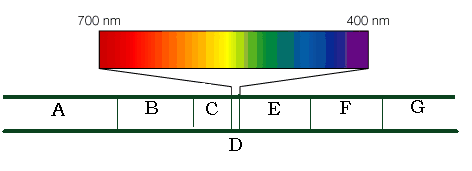
30. (7) Identify the region of the spectrum (shown above) representing each of the
following kinds of radiation:
visible light
x-rays
infrared
ultraviolet
microwave
radio
gamma rays
31. (2) Which kind of electromagnetic radiation represents the highest energies? _____________________
32. (2) Which kind of radiation represents the highest frequencies? __________________________________
33. (2) Which kind of radiation represents the shortest wavelengths? _________________________________
34. (2) Which region of the spectrum represents the peak of the Sun's thermal
radiation curve? _______
35. (1) CCDs are used in astronomy
A) as silicon chips sensitive to light.
B) as electronic detectors.
C) to image objects
D) as charge-coupled devices.
E) all of the above.
36. (1) Telescopes created with glass lenses are called
A) regenerators.
B) refractors.
C) diffractors.
D) reflectors.
37. (1) A telescope's light-collecting area can be increased by
A) using an eyepiece with a longer focal length.
B) increasing the diameter of the telescope.
C) using an eyepiece with a shorter focal length.
D) increasing the length of the telescope.
38. (1) A telescope's magnification can be increased by
A) using an eyepiece with a longer focal length.
B) increasing the diameter of the telescope.
C) using an eyepiece with a shorter focal length.
D) increasing the length of the telescope.
39. (1) In astronomy, red filters are used to
A) block out red light.
B) monitor hot objects.
C) cool down the telescope
D) allow only red light to enter a telescope.
E) None of these is correct.
40. (1)Compared to a refracting telescope, a reflecting telescope
A) uses lenses instead of mirrors.
B) uses mirrors instead of lenses
C) is less commonly used for astronomical research.
D) has more trouble seeing through atmospheric turbulence.
E) cannot be built as large.
Examine the following spectra - a spectrum of a gaseous nebula and spectra from
4 laboratory emission tubes (much like you viewed in class):

41. (2) Which elements are present in the spectrum of the gaseous nebula?
42. (2) What method did you use to answer the previous question?
43. (4) How does this relate to the way astronomers identify elements in celestial
objects?
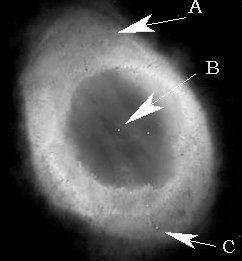
Shown above is an image of the Ring Nebula. "A" represents the gaseous nebula; "B"
represents the hot (100,000 degree Kelvin) white dwarf (thermal radiator) seen with
no gas in front of it; and "C" represents a star much hotter than the nebula but
lying hundreds of light years beyond the nebula.
44. (3) For which of these objects would you expect to observe
a continuous spectrum? ____________
an emission spectrum? ____________
an absorption spectrum? ___________
45. (20pts) Definitions (1 points each) Pick 10 of the following terms and
define them using totally your own words. Use each word in a well-constructed
sentence.
galaxy
right ascension
star
celestial sphere
Astronomical unit
zodiac
constellation
declination
Altitude
Azimuth
Ecliptic
Zenith



