Work and Energy and Momentum
Select the best possible answer.
1. Equal forces are used to move blocks A and B across the floor. Block A has twice the mass of block B, but block B moves twice the distance moved by block A. Which block has the greater amount of work done on it?
a. Block A.
b. Block B.
c. The same amount of work is done on both blocks.
d. Block A or B depending on the weight of the blocks.
2. A string is used to pull a block across the floor as shown in the figure. Is the total force involved in doing work, or just a portion of the force?
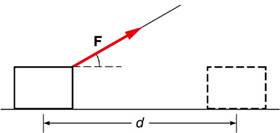
a. The total force F is involved in doing work.
b. A portion that is equal to the horizontal component of F is involved in doing work.
c. A portion that is equal to the vertical component of F is involved in doing work.
d. No portion of F is involved in doing work.
3. In the situation shown in the previous question, suppose there is a friction force as the block slides across the floor. Does this force do work on the block?
a. No; the work done by the friction force is zero in this case.
b. No; the friction force is not parallel to the direction of motion and no work will be done.
c. Yes; the friction force will do negative work on the block.
d. Yes; the friction force will do positive work on the block.
4. A pendulum is pulled back from equilibrium (center) position and then released. What form of energy is added to the system prior to its release?
a. Gravitational potential energy.
b. Kinetic energy.
c. Elastic potential energy.
d. Chemical energy.
5. Consider the pendulum of the previous question. At what points in the motion of the pendulum after release is its kinetic energy the greatest?
a. At the point of release.
b. At the center of motion.
c. At the midpoint between center and the point of release.
d. At the midpoint between the center and the point of maximum height.
6. A 200-kg rock is pulled at a constant speed out of a well of depth 20 meters in 4 seconds by a motor. The power used by the motor is
a. 4000 watts.
b. 9800 watts.
c. 1000 watts.
d. 16000 watts.
7. A 100-kg box is pushed with a force of 35 lb. If the box is displaced by 6 meters, the amount of work done on the box is:
a. 3500 ft.lb.
b. 600 kg.m.
c. 210 Joules.
d. 924 Joules.
8. If the box of previous question is raised to a height of 1.5 meters, its potential energy is:
a. 1470 Joules.
b. 150 Joules.
c. Zero.
d. 3500 Joules.
9. If the box of previous question is dropped, its K.E. right before coming to rest is:
a. 1470 Joules.
b. 150 Joules.
c. Zero.
d. 3500 Joules.
10.
A lawn mower engine is
rated as 5 hp. This means that the
engine:
a. Can perform 5 joules of work per second.
b. Can perform 3730 joules of work per second.
c. Can perform 550 joules of work per second.
d. Can perform 746 joules of work per second.
11. A woman does 160 J of work to move a table 4 m across the floor by applying a horizontal force. What is the magnitude of the force that the woman applied?
a. 160 N.
b. 40 N.
c. 640 N.
d. 4 N.
12. A rope applies a horizontal force of 180 N to pull a crate a distance of 2 m across the floor. A frictional force of 120 N opposes this motion. What is the work done by the rope?
a. 180 J.
b. 120 J.
c. 360 J.
d. 240 J.
13. In the previous question, what is the magnitude of work done by the friction force?
a. 180 J.
b. 120 J.
c. 360 J.
d. 240 J.
14. In the previous question, what is the total work done on the crate?
a. 180 J.
b. 120 J.
c. 360 J.
d. 240 J.
15. A 0.4-kg ball has a velocity of 20 m/s. What is the kinetic energy of the ball?
a. 8 J.
b. 100 J.
c. 50 J.
d. 80 J.
16. How much work is required to stop the ball of the previous question?
a. 8 J.
b. 100 J.
c. 50 J.
d. 80 J.
17. Which requires more work: lifting a 2-kg rock to a height of 4 m without acceleration, or accelerating the same rock horizontally from rest to a speed of 10 m/s?
a. Lifting the rock.
b. Accelerating the rock.
c. Both require same amount of work.
d. Accelerating the rock because the required work for lifting it is zero.
18. Ignoring air resistance, what is the kinetic energy of a 2-kg ball dropped from rest after 1 second?
a. 19.6 J.
b. 9.80 J
c. 96 J
d. 14.7 J
19. A car traveling at a speed of 40 km/hr increases its speed to 80 km/hr. As a result its kinetic energy increases:
a. 2 times.
b. 4 times.
c. 8 times.
d. Stays the same.
20. The unit of energy in the metric system (SI) is:
a.
b. ft.lb.
c. Joule.
d. Watt.
21. Does the length of time that a force acts on an object have any effect on the strength of the impulse produced?
a. Yes, the impulse is directly proportional to the time of contact.
b. Yes, the impulse is inversely proportional to the time of contact.
c. No, the impulse is independent of the time of the contact.
d. None of the above.
22. Is it possible for a baseball to have as large a momentum as a much more massive bowling ball?
a. The bowling ball will always have a larger momentum than a baseball.
b. Since the bowling ball is much heavier, the baseball will always have a larger momentum.
c. If the baseball has a sufficiently large velocity, it could have the same momentum.
d. The only time that they have the same momentum is when they are at rest.
23. What is the advantage of a padded dashboard compared to a rigid dashboard in reducing injuries during collision?
a. Padded dashboards increase the time of contact, which reduces the force of injury.
b. Padded dashboards decrease the time of contact, which reduces the force of injury.
c. Padded dashboards decrease the velocity of crash, which reduces the force of injury.
d. Padded dashboards reduce the impulse, which reduces the force of injury.
24. A compact car and a large truck have a head-on collision. During the collision, which vehicle experiences a larger force of impact?
a. The truck.
b. The compact car.
c. Both experience the same impact force.
d. We cannot say. It depends on the velocity of the collision.
25. In the previous question, which vehicle experiences a greater impulse?
a. The truck.
b. The compact car.
c. Both experience the same impulse.
d. We cannot say. It depends on the velocity of the collision.
26. In the previous question, which vehicle experiences the greater acceleration?
a. The truck.
b. The compact car.
c. Both experience the same acceleration.
d. We cannot say. It depends on the velocity of the collision.
27. In order to reduce the "sting" in catching a hard
ball one usually:
a. Increases momentum change.
b. Increases the contact force.
c. Increases the impulse.
d. Increase the contact time.
28. What is the momentum of a 1200-kg car traveling with a speed 27 m/s?
a. 32400 kg.m/s.
b. 1200 kg.
c. 11760 N.
d. 27 m/s.
29. A 0.12-kg ball traveling with a speed of 40 m/s is brought to rest in a catcher's mitt in a time of 0.2 seconds. What is the size of the force exerted by the ball on the mitt?
a. 0.12 kg.
b. 1.18 N.
c. 4.8 kg.m/s.
d. 24 N.