Falling Objects and Projectile Motion
Select the best possible answer.
1. The following diagrams shows the position at the interval of 0.1 second of a ball moving from left to the right in three different motions. In which case the ball is accelerating?
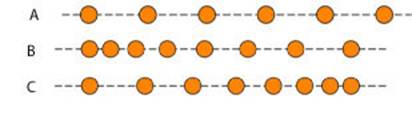
a. In diagram A the ball is not accelerating, but it is accelerating in diagrams B and C.
b. In diagrams A and C the ball is not accelerating, but it is accelerating in diagram B.
c. In diagrams A and B the ball is not accelerating, but it is accelerating in diagram C.
d. In all three diagrams the ball is accelerating.
2. A lead ball and an aluminum ball, each 1 inch in diameter, are released simultaneously from the same height, and allow to fall to the ground. Assume negligible air resistance. Which of these balls has a greater acceleration?
a. Lead ball.
b. Aluminum ball.
c. Both have the same acceleration.
d. The balls are not accelerating because they are not changing their direction of motion.
3. In the previous question, which one of the balls has a higher acceleration if air resistance is taken into account?
a. Lead ball.
b. Aluminum ball.
c. Both have the same acceleration.
d. Air resistance only affects their velocities but not their acceleration that remains zero.
4. Two identical pieces of paper, one crumpled into a ball and the other left uncrumpled, are released simultaneously from the same height falling through the air. Which one reaches the floor first?
a. The crumpled piece.
b. The uncrumpled piece.
c. Both reach the floor at the same time.
d. We cannot say. It could be either piece depending on the released height.
5. If the two pieces of the paper in the previous question are released inside a large evacuated tube, which one will reach the bottom of the tube first?
a. The crumpled piece.
b. The uncrumpled piece.
c. Both reach the floor at the same time.
d. We cannot say. It could be either piece depending on the released height.
6. A rock is dropped from the top of a diving board into a swimming pool below. How does the distance traveled by the rock in a 0.1-second interval near the top of its flight compare to the distance covered in 0.1-second interval just before it hits the water?
a. The distance before it hits is larger.
b. The distance near its top is larger.
c. The two distances are the same.
d. We cannot say because the height of the diving board is not given.
- The graph shows the velocity plotted against time for a certain falling object. Is the acceleration of this object constant?
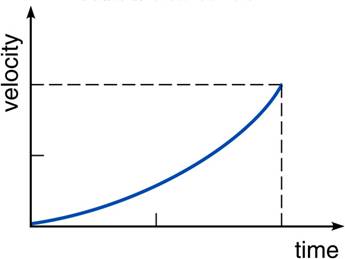
a. The acceleration is constant because the velocity is changing.
b. The acceleration is zero because the direction of motion remains constant.
c. The acceleration is constant but then start changing toward the end.
d. The acceleration is not constant because the change in velocity per interval is different.
8. A ball is thrown downward with an initial velocity of 6 m/s. Another ball just dropped from the same height. Which ball has a larger acceleration? Assume negligible air resistance.
a. The thrown ball.
b. The dropped ball.
c. Both have the same acceleration.
d. The answer depends on the height where the balls are released or thrown.
9. If an object falling freely downward were somehow equipped with an odometer to measure the distance it travels, then the amount of distance it travels each succeeding second would be:
a. Constant.
b. Less and less.
c. Greater than the second before.
d. For the first few seconds the distance remains constant, and then it starts increasing.
10. If an object falls with constant acceleration, the velocity of the object must:
a. Be constant also.
b. Continuously change by the same amount each second.
c. Continuously change by varying amounts depending on its speed.
d. Continuously decrease.
11. A heavy object and a light object are dropped from the same height and at the same time from rest in a vacuum. The heavier object reaches the ground:
a. Sooner than the lighter object.
b. At the same time as the lighter object.
c. Later than the lighter object.
d. Either (a) or (c) depending on the height they are dropped.
12. Drop a rock from a 5-m height and it accelerates at 10 m/s2 and strikes the ground 1 s later. Drop the same rock from a height of 2.5 m and its acceleration of fall is:
a. About half.
b. The same.
c. More.
d. Zero because of shorter distance.
13. Suppose the rock of the previous question is thrown downward from the top of a high cliff with an initial speed of 6 m/s. What is the speed of the thrown rock after 1 second into its flight?
a. 6 m/s.
b. 16 m/s.
c. 4 m/s.
d. Zero.
14. A ball is thrown straight upward. At the very top of its flight, which one of the following statements is correct?
a. Its velocity and acceleration are zero.
b. Its acceleration is zero but its velocity is not zero.
c. Its velocity is zero but its acceleration is not zero.
d. Both its velocity and acceleration are not zero.
15. A ball is thrown straight upward and then returns to the ground. Does the acceleration change direction during this motion?
a. As the ball goes up the acceleration is upward and as it goes down the acceleration is downward.
b. As the ball goes up the acceleration is downward and as it goes down the acceleration is upward.
c. The acceleration of the ball is always directed upward throughout its flight.
d. The acceleration of the ball is always directed downward throughout its flight.
16. A ball rolling rapidly along a tabletop rolls off the edge and falls to the floor. At the exact instant that the first ball rolls off the edge, a second ball is dropped from the same height. Which ball reaches the floor first?
a. The rolling ball.
b. The dropped ball.
c. Both reach at the same time.
d. Could be either ball depending on the height of the table.
17. A cannonball fired at an angle of 70o to the horizontal stays in the air longer than one fired at 45o. Which one travels a longer horizontal distance?
a. The 70o ball.
b. The 45o ball.
c. Both balls will travel the same horizontal distance.
d. Depends on how much longer is the 70o ball in the air.
18. A football is thrown as a long pass. Consider the ball when it reaches the highest point on its path. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The velocity of the ball at this point is zero, but its acceleration is not zero.
b. The acceleration of the ball at this point is zero, but its velocity is not zero.
c. The vertical component of the velocity is zero, but its horizontal component is not zero.
d. The horizontal component of the velocity is zero, but its vertical component is not zero.
19. A soccer ball is kicked with an initial angle of 25o. It travels a horizontal distance (i.e. range) of 30 m. Assuming the same initial speed, at what other angle it should be kicked in order to have the same range?
a. 65o.
b. 35o.
c. 45o.
d. 75o.
20. A steel ball is dropped from a diving board. What is the velocity of the ball after 0.8 seconds into its flight? Assume negligible air resistance.
a. 9.8 m/s.
b. 0.8 m/s.
c. 10.6 m/s.
d. 7.8 m/s.
21. What is the acceleration of the steel ball of the previous question after 0.8 seconds?
a. 9.8 m/s2.
b. 0.8 m/s2
c. 10.6 m/s2.
d. 7.8 m/s2.
22. For the steel ball of the previous question, through what distance does the ball fall in the first 0.8 seconds of its flight?
a. 6.2 m.
b. 9.8 m.
c. 3.1 m.
d. 10.6 m.
23. A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 15 m/s. What is its velocity 1 second later? (Give the approximate value and the direction. Assume negligible air resistance)
a. 5 m/s upward.
b. 9.8 m/s downward.
c. 15 m/s upward.
d. 3.1 m/s downward.
24. For the ball of the previous question, approximately how long will it take for the ball to reach the its highest (top) point?
a. 0.5 s.
b. 1.5 s.
c. 2.0 s.
d. 2.5 s.
25. For
the ball of the previous question, how high above the ground is the ball when
it reaches the
a. 9.8 m.
b. 4.9 m.
c. 22.5 m.
d. 11.0 m.
26. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground with a speed of about:
a. 5 m/s.
b. 10 m/s.
c. 15 m/s.
d. 20 m/s.
27. It takes 6 seconds for a stone to fall to the bottom of a mineshaft. How deep is the shaft?
- About 60 m
- About 120 m
- About 180 m
- More than 200 m
28. A projectile is fired straight up at a speed of 10 m/s. How long is the time it takes to reach the top of its path (assume negligible air resistance)?
- 1 s.
- 2 s.
- 10 s.
- Not enough information to estimate.
29. Disregarding air drag, how fast must you toss a ball straight up in order for it to take 2 seconds to return to the level from which you tossed it?
- 5 m/s
- 7.5 m/s
- 10 m/s
- 15 m/s
30. A
bullet is dropped from the top of the
- The fired bullet is greater.
- The dropped bullet is greater.
- Each bullet is 9.8 m/s2.
- Both bullets move with a constant velocity such that their acceleration is zero.