Instructions: Buoyancy
Animation: Buoyancy.
Related Concepts: Pressure in fluids, density, volume,
Archimedes’ principle.
Description: The buoyant force is the force acting on
objects submerged in fluids. The reason for this force is the
unequal pressure acting on the top surface and the bottom surface
of the submerged object. This unequal pressure gives rise to a
net upward force which is called the buoyant force. The magnitude
of this force is equal to the weight of the displaced liquid.
This last statement is called the Archimedes’ principle, but
it can be proved easily.
The primary idea of this animation is to illustrate the buoyancy
by measuring the buoyant force acting on objects of different
weights and sizes (volumes).
Activity: Start the “Buoyancy” program by the clicking on
the appropriate link. Click on the “information button” to learn more
about the steps involved in running the animation. Study the stage and familiarize
yourself with the experiment by checking the menus and different buttons. Once
you are ready go to the next section and answer the questions.
Questions:
Carefully study all pages of review lesson “Review of Buoyancy”. This serves as a
review of the concepts involved in the calculation of the buoyant force. Make
sure that you understand the sample calculation done on page 3 of the animation.
Now go back and open the computer animation “Buoyancy”.
Click on the box “show forces” and then click on one of the objects
on the table and move it into the water container. Follow the procedure as described
before in the “Density”. As you move the object slowly into the water,
take note the two arrows which represent the buoyant force (red arrow) and the
weight (green arrow).
1) As the object is slowly submerged, what happens to the length of the arrow
representing the buoyant force? What does this imply for the buoyant force? Explain
your reasoning.
2) Once the object is fully submerged, what happens to the red arrow? What happens
to the buoyant force? Explain.
3) In questions (1) and (2) describe what happens to the arrow representing weight
of the object. Explain.
4) Move all objects except the wooden piece into the water and use the results
to calculate the buoyant force acting on them. In each case, what is the net force
acting on the objects?
5) Click on the wooden piece and move it into the water such that it is completely
submerged. Release the wood under the water. Notice that it will move upwards
and stays afloat. Check the length of the arrows for buoyant force as the wood
moves upwards and finally floats. What do you conclude?
6) The following equation gives the percentage of the volume of objects floating
in liquids:
( volume of the object in the
water)/(total volume of the object) = (density of the
object)/(density of the liquid)
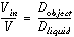
Verify this relationship for the wooden piece as it floats in
water.