Newton's Laws of Motion
Select the best possible answer.
1. Why did Aristotle believe that heavier objects fall faster than lighter objects?
a. Because less air resistance acts on heavier objects.
b. Because a larger force acts on heavier objects.
c. Because heavier objects should naturally move faster.
d. Because heavier objects have larger mass and larger velocity.
2. Two equal net forces act on two different objects, one of which has a mass ten times as large as the other. Compare the accelerations of the two objects?
a. The acceleration of the massive object is 10 times the acceleration of the light object.
b. The acceleration of the massive object is 1/10 the acceleration of the lighter object.
c. The acceleration of the massive object is the same as the acceleration of the light object.
d. The acceleration of both objects is actually zero.
3. Did
Galileo develop a more comprehensive theory of motion than that of
a. No,
b. Yes,
Galileo's theory of motion is more comprehensive than that of
c. Galileo did not develop any theory of motion. He work is mostly on the subject of art.
d. Galileo
and
4. A 3-kg block is observed to accelerate at a rate twice that of a 6-kg block. How do the net forces acting on these block compare?
a. The net force acting on the 3-kg block is the same as the net force on 6-kg block.
b. The net force acting on the 3-kg block is twice the net force on the 6-kg block.
c. The net force acting on the 3-kg block is half the net force on the 6-kg block.
d. The net force acting on the 3-kg block is 4 times the net force on the 6-kg block.
5. Two equal forces act on a block as shown in the diagram. Is it possible that the block is moving?

a. The block cannot move because there is a zero net force acting on it.
b. The block cannot move because its net acceleration is zero.
c. The block can move because any force produces a motion.
d. The block can be moving if its motion had started before the net force balances to zero.
6. Is it possible for the block of the previous question to have a net horizontal acceleration?
a. No, because the net force is zero.
b. No, because the object cannot be moving under the condition shown in the diagram.
c. Yes, because according to the second law, forces give rise to accelerations.
d. Yes, but the acceleration depends on the mass of the block.
7. Two equal forces act on an object of mass m, in the directions pictured in the diagram below. If these are the only forces involved, will the object be accelerated?
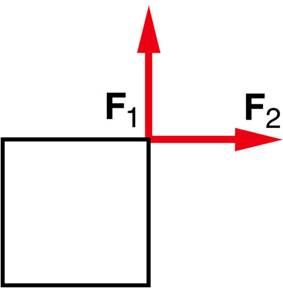
a. The acceleration is zero because the net force is zero.
b. The object moves in the direction of force F1with an acceleration a = F1/m.
c. The object moves in the direction of force F2with the acceleration a = F2/m.
d. The object moves in the direction of the net force with the acceleration a = Fnet/m.
8. Is the mass of an object the same thing as its weight?
a. Mass is a measure of inertia or while weight is the gravitational force acting on an object.
b. Mass and weight are the same. They can be interchanged in the Newton's second law.
c. Mass of an object is exactly equal to how much that object weighs.
d. Mass or weight is the same. They are equal to the amount of matter within an object.
9. If a rock is transported from the earth to the moon, will either its mass or its weight change?
a. Its weight and mass will change. They become 1/6th of their value on the earth.
b. Its mass will remain the same, but its weight will become 1/6th of its weight on the earth.
c. Its weight will remain the same, but its mass will become 1/6th of its mass on the earth.
d. Since moon has no gravity, both its weight and mass will become zero.
10. Two identical cans, one filled with lead shots and one with feathers, are dropped from the same height. Which can experiences the greater force due to the gravity of the earth?
a. The lead can.
b. The feathers can.
c. Both will experience the same force.
d. Since feathers are light, the feathers can will experience zero force.
11. In the previous question about dropped cans, which one experiences a larger gravitational acceleration?
a. The lead can.
b. The feathers can.
c. Both will experience the same acceleration.
d. Since feathers are light, the feathers can will experience zero acceleration.
12. A boy sits on the floor. What two vertical forces act on the boy?
a. An action and reaction force act on the boy.
b. A friction force and reaction force act on the boy.
c. Air resistance and the friction due to floor act on the boy.
d. The gravitational pull of the earth and the reaction force of the floor act on the boy.
13. A car is driven on a level surface. What force acting on the car is responsible for accelerating it forward?
a. The force that engine applies to the car.
b. The force of friction of the road on the car.
c. The horizontal reaction force of the road on the car.
d. The horizontal force of the car on the road.
14. A ball hangs from a ceiling and stays at rest as shown. What forces act on the ball?
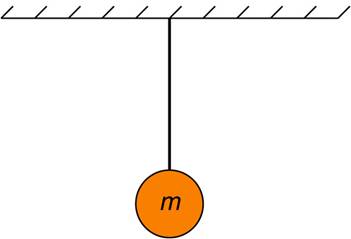
a. The force of air resistance.
b. The force of gravity and the string tension acting on the ball.
c. The force of gravity and the force of ceiling on the ball.
d. The force of gravity, the string tension, and the force of the ceiling on the ball.
15. What is the net force acting on the ball of the previous question?
a. The net force is zero.
b. The net force is equal to the weight of the ball and is downward.
c. The net force is equal to the pull of the string and is upward.
d. The net force is equal to the pull of the ceiling on the string and is upward.
16. The tendency of objects to resist a change in motion is called:
a. Friction
b. Velocity
c. Inertia
d. Acceleration
17. In the previous question, the inertia of an object is measured by its:
a. Speed.
b. Velocity.
c. Mass.
d. All of these.
18. The force required to maintain a body at constant velocity in free space is equal to:
a. The mass of the body.
b. Zero.
c. The weight of the body.
d. The force required stopping it.
19. A heavy man and a light man parachute together from a high-flying plane. The first man to attain zero acceleration will be the:
a. Light man
b. Heavy man
c. Both will attain zero acceleration at the same time.
d. Both will have zero acceleration from the start of their fall to the time of landing.
20. In which case would you have the largest mass of gold? If you chunk of gold weighed 1 N on the:
a. Moon
b. Earth
c. Planet Jupiter
d. Would be the same on each.
21. While a ship moves toward the right at constant velocity, a seaman atop the mast drops a stone which freely falls to position:
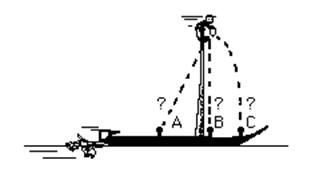
a. Path A.
b. Path B.
c. Path C.
d. None of the above.
22. A 200-N weight hangs motionless from a string that is attached to the ceiling. The net force acting on the weight is:
a. Zero.
b. 100 N.
c. 200 N.
d. 100 kg.
23. In the previous question, if the string breaks, the net force acting on the weight will be: (assume no air resistance)
a. Zero.
b. 100 N.
c. 200 N.
d. 100 kg.
24. The force that accelerates a rocket in outer space is exerted on the rocket by the:
a. Rocket's engine.
b. Rocket's wings.
c. Atmospheric pressure.
d. Exhaust gases.
25. An archer shoots an arrow. Consider the action force to be exerted by the bowstring against the arrow. The reaction to this force is the:
a. Air resistance against the arrow.
b. Friction of the ground against the archer's feet.
c. Grip of the archer's hand on the bow.
d. arrow's push against the bowstring.
26. A player catches a ball. Consider the action force to be the impact of the ball against the player's glove. The reaction to this force is:
a. Player's grip on the glove.
b. Force the glove exerts on the ball.
c. Friction of the ground against the player's shoes.
d. Muscular efforts in the player's arms.
27. A player hits a ball with a bat. The action force is the impact of the bat against the ball. The reaction to this force is the:
a. Air resistance on the ball.
b. Weight of the ball.
c. Force of the ball against the bat.
d. Grip of the player's hand against the ball.
28. A single force of 40 N acts upon a 5-kg block. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block?
a. 9.8 m/s2.
b. 8 m/s2.
c. 0.12 m/s2.
d. 0 m/s2.
29. A ball with a mass of 1.5 kg is observed to move with an acceleration of 6 m/s2. What is the size of the net force acting on the ball?
a. 0 N.
b. 24.5 N.
c. 2.5 kg.
d. 9 N.
30. A 2.5-kg block being pulled across a table by a horizontal force of 80 N also experiences a frictional force of 5 N. What is the acceleration of the block?
a. 32 m/s2.
b. 30 m/s2.
c. 9.8 m/s2.
d. 2.0 m/s2.
31. What is the weight of a 40-kg mass?
a. 40 kg.
b. 9.8 N.
c. 392 N.
d. 40 N.
32. What is the mass of a 540-N object?
a. 540 kg.
b. 9.8 kg.
c. 540 N.
d. 55.1 kg.
33. Jennifer has a weight of 110 lb. What is her weight in newtons?
a. 110 N.
b. 484 N.
c. 25 N.
d. 9.8 N.
34. Who has the larger mass, a man weighing 145 lb or one weighing 735 N?
a. The 145-lb man.
b. The 735-N man.
c. They both have the same mass.
d. We cannot say. It depends on how tall they are!
35. A 60-kg woman in an elevator is accelerating upward at a rate of 1.2 m/s2. What is the gravitational force acting on the woman?
a. 60 kg.
b. 588 N.
c. 660 N.
d. 72 N.
36. What is the net force acting on the woman of the previous problem?
a. 60 kg.
b. 588 N.
c. 660 N.
d. 72 N.
37. What is the normal force pushing upward on the woman of the two previous questions?
a. 60 kg.
b. 588 N.
c. 660 N.
d. 72 N.