Magnetism
Select the best possible answer.
1. The north pole of a bar magnet is brought near the north pole of a second bar magnet lying on a table. How will the second magnet tend to move?
a. The magnet lying on the table will be attracted toward the first magnet.
b. The magnet lying on the table will be repelled from the first magnet.
c. The magnet lying on the table will be unaffected by the first magnet.
d. Either (a) or (b) depending on the distance between the poles.
2. If the distance between the south poles of two bar magnets is reduced to half its original value, what would happens to the force between the magnets?
a. The force between the magnets will remain the same as the original value.
b. The force between the magnets will be doubled.
c. The force between the magnets will be quadrupled.
d. The force between the magnets will be halved.
3. We visualized the magnetic field of the earth by imagining that there is a bar magnet inside the earth. Why did we draw this magnet with its south pole pointing north?
a. The north geographic pole of the earth attracts the south magnetic pole.
b. The south magnetic pole attracts the north pole of a compass.
c. The south magnetic pole repels the north pole of a compass.
d. This is just for visualization. Actually, the south magnetic pole should be in the southern hemisphere.
4. A horizontal wire is oriented along a north-south line, and a compass is placed above it. An electric current flows north through the wire. Will the needle of the compass deflect?
a. The needle will remain directed toward north. The current has no effect on the compass.
b. The needle will be deflected away from north and will be aligned with the south direction.
c. The needle will be deflected away from north toward a north- west direction.
d. The needle will be deflected away from north toward a north- east direction.
5. A positive charge particle is momentarily at rest in a magnetic field. Is there magnetic force acting on this particle?
a. Yes; all charged particles in a magnetic field are acted upon by a magnetic force.
b. Yes; and the magnetic force will cause the particle to start moving.
c. No; a charge particle at rest is not affected by a magnetic field.
d. No; positively charged particles are not affected by magnetic fields.
6. Is a magnetic flux the same as a magnetic field?
a. No; the magnetic flux is proportional to the number of magnetic field lines through the area of a loop.
b. No; the magnetic flux is the current that flows around a loop and creates a magnetic field.
c. Yes; the magnetic flux is basically the same as the magnetic field that exists in space.
d. Yes; the magnetic flux is the magnetic field produced by bar magnets.
7. Can a transformer be use, as shown in the figure, to step up the voltage of a battery?
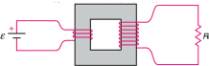
a. Yes; there are more windings in the secondary than the primary. The output voltage will be higher.
b. Yes; the battery creates a changing magnetic field and the device performs like a step up transformer.
c. No; the primary and the secondary circuits are not connected and the device will not work as a transformer.
d. No; the battery produces a constant magnetic field. There will be no induced voltage in the secondary.
8. Can we use a step up transformer to increase the amount of electrical energy drawn from an alternating current source?
a. Yes; a step up transformer increases the output voltage and the energy.
b. Yes; a step up transformer increases the output current and the energy.
c. No; a step up transformer increases the output voltage and current but not the energy.
d. No; a step up transformer increases the output voltage but not the output energy.
9. The source of all magnetism is:
a. Tiny pieces of iron.
b. Tiny domains of aligned atoms.
c. Ferromagnetic materials.
d. Moving electric charge.
10. Several paper clips dangle from the north pole of a magnet. The induced pole in the bottom of the lowermost paper clip is a
a. North pole.
b. South pole.
c. North or south pole - no difference really.
d. The pole at the bottom of the clip is not magnetic.
11. When a bar magnet is broken in two, each piece is:
a. As magnetic as the original magnet.
b. Actually stronger than the original magnet.
c. At most half as strong as the original magnet.
d. No longer magnetic.
12. A device that transforms electrical energy to mechanical energy is a:
a. Generator.
b. Motor.
c. Transformer.
d. Magnet.
13. A device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy is a:
a. Generator.
b. Motor.
c. Transformer.
d. Magnet.
14. A transformer has 15 turns of wire in the primary and 60 turns in the secondary. The transformer is connected to an ac source of 110 volts. What is the output voltage in the secondary?
a. 110 V.
b. 27.5 V.
c. 440 V.
d. 220 V.
15. In the previous question, if a current of 8 A flows through the primary circuit, what is the induced current in the secondary?
a. 2 A.
b. 8 A.
c. 4 A.
d. 1 A.
16. A step-down transformer converts a voltage of 120 V to 6 V. If there are 300 turns in the primary, how many turns should there be in the secondary?
a. 300 turns.
b. 6000 turns.
c. 15 turns.
d. 150
turns.