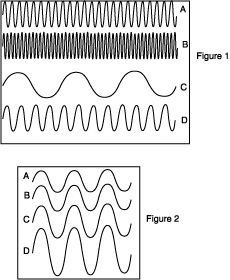
 |
a) wave A
b) wave B
c) wave C
d) wave D
Review Questions: EM Waves and Light
Answers
1) An electromagnetic wave can be produced by
a) a static positive or negative electric charge
b) a steady current in a wire
c) changing electric current
d) a strong magnet
Reasoning: A changing electric current involves ekectriuc charges in motion with acceleration. Whenever electric charges move with acceleration, they emit radiation in the form of EM waves. See chapter 26, pages 496-497.
2) Light of shorter wavelength than that to which eye is sensitive is called
a) infrared
b) ultrasonic
c) microwaves
d) ultraviolet
3) Microwaves are
a) sound waves
b) electromagnetic waves with wavelength of a few mm to several cm
c) EM waves with wavelength of about one-millionth of a meter
d) EM waves with wavelength of about one-million meters
Reasoning: Check figure 26.3 and you will notics that microwaves have frequencies from f = 109 Hz to 1011 Hz. Therefore, the wavelength = c/f = 300,000,000/109=0.003 meters = 3 mm.
4) A suntan is a protective mechanism against which type of radiation?
a) infrared
b) visible
c) ultraviolet
d) X-rays
Reasoning: Ultraviolet radiation (suntan)darkens the skin color and as a result less UV radiation is absorbed by the skin.
5) A particular FM station broadcasts at 92 MHz. What is the wavelength of this wave?
a) 300,000 meters
b) 3.26 meters
c) 92 meters
d) 1 cm
Reasoning:Use the same calculation as presented for question 3.
6) Which one of following EM waves has the highest frequency?
a) ultraviolet
b) infrared
c) x-rays
d) gamma rays
7) The ozone layer
a) reflects all EM waves
b) reflects high frequency radio waves
c) reflects low frequency radio waves
d) absorbs ultraviolet light in sunlight
8) The wavelength of an EM wave with a frequency of 1017 Hz is:
a) 3 m
b) 3 nm
c) 30 mm
d) 3 Ao
Reasoning:Using the calculation shown in question 3 gives the wavelength = 3 x 10-9 m. This is the same as 3 nm (or 3 nanometers).
9) The wavelength of a red light with a frequency of 3.8 x 1014 Hz is:
a) 3.8 m
b) 789 nm
c) 300,000 km/s
d) 3.8 x 1014 m
10) If an electron vibrates up and down 1000 times each second, it generates an EM wave having a
a) period of 1000 second
b) speed of 1000 m/s
c) wavelength of 1000 m
d) freaquency of 1000 Hz
11) The frequency of an x-ray with a wavelength of 0.1 nm is, (hint: 1 nm = 10-9 m)
a) 3 Hz
b) 30 Hz
c) 3 x 1017 Hz
d) 3 x 1018 Hz
Reasoning: Again use the relationship: wavelength = c/f. In this case wavelength is given. Thus solving for f, we have: f = c/wavelength.
12) Red light is used to form a two-slit interference pattern on a screen. As the two slits are moved further apart, the separation of the bright bands on the screen
a) decreases
b) increases
c) go to zero
d) remains unchanged
Reasoning: Refer to the computer experiments and see how this works out!
13) Which one of the following colors produces the narrowest interference pattern?
a) orange
b) green
c) violet
d) red
14) The observation that the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by red light is wider than the one produced by blue light indicates that the red light
a) has a longer wavelength
b) has a shorter wavelength
c) has a higher frequency
d) has a lower intensity
15) Which of the following effects occurs for transverse waves but not for longitudinal waves?
a) interference
b) diffraction
c) polarization
d) reflection
Reasoning: See pages 576-577 for details.
16) If all of the labels have come off the sunglasses in the drug store, you could tell which ones were polarized by
a) feeling their surfaces
b) scratching the lenses to see they are plastic
c) looking at sunlight reflected from water
d) looking at the light from the incandescent lamps in the store
Reasoning: The reflected sunlight will be partially polarized!
17) Polarized sunglasses
a) absorb both the horizontal and vertical polarizations
b) absorb the horizontal but transmit the vertical polarization
c) rotate both the horizontal and vertical polarizations
d) absorb the vertical but transmit the horizontal polarization
Reasoning: See figure 29.34 for details.
18) Two waves are traveling towards each other along a rope. What occurs when they overlap one another?
a) diffraction
b) reflection
c) polarization
d) interference
19) Among the waves shown if Figure 1, which one has the highest frequency?
a) wave A
b) wave B
c) wave C
d) wave D
20) Among the waves shown if Figure 2, which one has the highest amplitude?
a) wave A
b) wave B
c) wave C
d) wave D
21) Among the waves shown if Figure 1, which one has the shortest wavelength?
a) wave A
b) wave B
c) wave C
d) wave D
22) Among the waves shown if Figure 2, which one has the longest wavelength?
a) wave A
b) wave B
c) wave C & D
d) ...all have the same wavelength
23) Waves diffract more when their wavelength is
a) long
b) short
c) .. diffraction is the same for long and short wavelengths
d) .. waves do not diffract. They only reflect.
Reasoning: See page 567.
24) In the double-slit experiment, the bright fringes at each spot on the screen are formed when the waves arriving from the slits are
a) producing destructive interference
b) producing constructive interference
c) polarized parallel to the plane of the screen
d) only longitudinal waves
25) In the double-slit experiment, the dark fringes at each spot on the screen are formed when the waves arriving from the slits are
a) producing destructive interference
b) producing constructive interference
c) polarized parallel to the plane of the screen
d) only longitudinal waves