There are 55 questions for 80 points total. Please pick the best answer for each
multiple choice question, filling in the correct bubble on your scantron. The "short answer" and "definitions" sections should be answered on the provided answer sheet. This test must accompany your scantron and answer sheet. Good luck.
Multiple Choice (1 point each) -- answer on the scantron
1) Which of the following has your "address" in the correct order?
- you, Earth, Local Group, Local Supercluster, solar system, Milky Way
- you, Earth, solar system, Local Group, Milky Way, Local Supercluster
- you, Earth, solar system, Milky Way, Local Group, Local Supercluster
- you, Earth, solar system, Milky Way, Local Supercluster, Local Group
- you, Earth, solar system, Local Group, Local Supercluster, Milky Way
2) What is the ecliptic?
- when the Moon passes in front of the Sun
- the Sun's apparent path along the celestial sphere
- the Sun's daily path across the sky
- the Moon's apparent path along the celestial sphere
- the constellations commonly used in astrology to predict the future
3) What is an astronomical unit?
- the average speed of the Earth around the Sun
- the length of time it takes the Earth to revolve around the Sun
- the diameter of the Earth's orbit around the Sun
- any basic unit used in astronomy
- the average distance from the Earth to the Sun
4) Which of the following statements about the celestial sphere is not true?
- From any location on Earth, we can see only half the celestial sphere at any one time.
- The Earth is placed at the center of the celestial sphere.
- The "celestial sphere" is just another name for our universe.
- When we look in the sky, the stars all appear to be located on the celestial sphere.
- The celestial sphere does not exist physically.
5) By locating the north celestial pole (NCP) in the sky, how can you determine your latitude?
- The azimuth of the NCP is the same as your latitude.
- The altitude of the NCP is the same as your distance from the North Pole.
- The altitude of the NCP is your angular distance from the North Pole.
- The altitude of the NCP is the same as your latitude.
- The azimuth of the NCP is the angular distance from the North Pole.
6) What makes the North Star, Polaris, special?
- It is the star straight overhead.
- It is the star directly on your northern horizon.
- It can be used to determine your longitude on Earth.
- It is the brightest star in the sky.
- It appears very near the north celestial pole.
7) What do scientists mean by observed facts?
- observations that can only be interpreted in one way
- observations that support a scientific theory
- statements that anyone would agree are obvious
- observations that a model does not have to predict
- statements that anyone can, in principle, verify for himself or herself
8) Which of the following statements about scientific models is true?
- A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature.
- All current models are correct.
- All models that explain nature well are correct.
- A model tries to represent all aspects of nature.
- A model can be used to explain and predict real phenomena.
9) Which of the following statements about scientific theories is not true?
- A theory is a model designed to explain a number of observed facts.
- A theory cannot be taken seriously by scientists if it contradicts other theories developed by scientists over the past several hundred years.
- If even a single new fact is discovered that contradicts what we expect according to a particular theory, then the theory must be revised or discarded.
- A theory must make predictions that can be checked by observation or experiment.
- A theory can never be proved beyond all doubt; we can only hope to collect more and more evidence that might support it.
10) Radiative energy is
- energy from nuclear power plants.
- energy of motion.
- energy carried by light.
- energy used in home radiators.
- heat energy.
11) Which object has the most kinetic energy?
- a 4-ton truck moving 50 km/hr
- a 2-ton truck moving 90 km/hr
- a 3-ton truck moving 70 km/hr
- a 1-ton truck moving 110 km/hr
- A, B, C, and D all have the same kinetic energy.
12) What does temperature measure?
- the average mass of particles in a substance
- the total number of particles in a substance
- the average size of particles in a substance
- the total potential energy of particles in a substance
- the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance
13) At extremely high temperatures (e.g., millions of degrees), which of the following best describes the phase of matter?
- a gas of rapidly moving molecules
- a plasma consisting of rapidly moving, neutral atoms
- a gas consisting of individual, neutral atoms, but no molecules
- a plasma consisting of positively charged ions and free electrons
- none of the above (at these extremely high temperatures, matter cannot exist)
14) Considering Einstein's famous equation, E = mc2, which of the following statements is true?
- A small amount of mass can be turned into a large amount of energy.
- You can make mass into energy if you can accelerate the mass to the speed of light.
- It takes a large amount of mass to produce a small amount of energy.
- One kilogram of mass represents 1 joule of energy.
- Mass can be turned into energy, but energy cannot be turned back into mass.
15) Which of the following scenarios correctly demonstrates the transformation of mass into energy as given by Einstein's equation, E = mc2?
- A burning piece of wood produces light and heat, therefore giving off radiative and thermal energy.
- When hydrogen is fused into helium, whether in the Sun or in a nuclear bomb, the mass difference is turned into energy.
- A mass raised to a great height has a lot of gravitational potential energy.
- When you boil a pot of water, it has a high heat content, or thermal energy.
- An object accelerated to a great speed has a lot of kinetic energy.
16) Which of the following statements correctly describes the law of conservation of energy?
- Energy can change between many different forms, such as potential, kinetic, and thermal, but it is ultimately destroyed.
- An object always has the same amount of energy.
- The total quantity of energy in the universe never changes.
- The fact that you can fuse hydrogen into helium to produce energy means that helium can be turned into hydrogen to produce energy.
- It is not really possible for an object to gain or lose potential energy, because energy cannot be destroyed.
17) When a rock is held above the ground, we say it has some potential energy. When we let it go, it falls and we say the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Finally, the rock hits the ground. What has happened to the energy?
- It is transformed back into gravitational potential energy.
- The energy goes to producing sound and to heating the ground, rock, and surrounding air.
- The rock keeps the energy inside it (saving it for later use).
- It is lost forever. Energy does not have to be conserved.
- The energy goes into the ground and, as a result, the orbit of the Earth about the Sun is slightly changed.
18) When an atom loses an electron, it becomes
- ionized.
- dissociated.
- sublimated.
- a plasma.
- an isotope.
19) When an atom has a different number of neutrons, we say it has one or more
- ionizations
- dissociations
- sublimations
- plasma types
- isotopes
20) An atom in an excited state contains more of what type of energy than the same atom in the ground state?
- gravitational potential energy
- mass-energy
- kinetic energy
- thermal energy
- electric potential energy
21) When an atom absorbs a photon containing energy, any of the following can happen except which?
- An electron moves from a lower energy level to an upper one.
- The atom becomes excited.
- An electron moves from an upper energy level to a lower one.
- The atom is ionized.
22) How can an electron in an atom lose energy to go from a higher energy level to a lower energy level?
- It loses kinetic energy.
- It absorbs a photon equal in energy to its own energy drop.
- It releases a photon equal in energy to its own energy drop.
- It exchanges gravitational potential energy for kinetic energy.
- It loses gravitational potential energy.
23) In which of the following cases would you feel weightless?
- while walking on the Moon
- while traveling through space in an accelerating rocket
- while falling from an airplane with your parachute open
- while falling from a roof
- None of the above.
24) Kepler's third law, p2 = a3, means that
- planets that are farther from the Sun move at slower average speeds than nearer planets.
- a planet's period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit.
- all orbits with the same semimajor axis have the same period.
- the period of a planet does not depend on its mass.
- All of the above are correct.
25) Kepler's second law, which states that as a planet moves around its orbit it sweeps out equal areas in equal times, means that
- planets have circular orbits.
- a planet's period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit.
- a planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun.
- the period of a planet does not depend on its mass.
- planets that are farther from the Sun move at slower average speeds than nearer planets.
26) Which of the following is not one of, nor follows directly from, Kepler's laws?
- As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
- More distant planets move at slower speeds.
- A planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from
the Sun.
- The force of attraction between any two objects decreases with the square of the
distance between their centers.
- The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
27) According to the universal law of gravitation, the force due to gravity is
- directly proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
- directly proportional to the distance between objects.
- inversely proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
- not dependent on the distance between objects.
- inversely proportional to the distance between objects.
28) According to the universal law of gravitation, if you triple the distance between two objects, then the gravitational force between them will
- decrease by a factor of 6.
- increase by a factor of 3.
- decrease by a factor of 9.
- increase by a factor of 9.
- decrease by a factor of 3.
29) According to the universal law of gravitation, if you double the masses of both attracting objects, then the gravitational force between them will
- not change at all.
- decrease by a factor of 4.
- decrease by a factor of 2.
- increase by a factor of 4.
- increase by a factor of 2.
30) The frequency of a wave is
- measured in hertz (Hz).
- equal to the speed of the wave divided by the wavelength of the wave.
- measured in cycles per second.
- the number of peaks passing by any point each second.
- All of the above.
31) The wavelength of a wave is
- the distance between where the wave is emitted and where it is absorbed.
- the distance between a peak of the wave and the next trough.
- how strong the wave is.
- equal to the speed of the wave times the wave's frequency.
- the distance between two adjacent peaks of the wave.
32) How are wavelength, frequency, and energy related for photons of light?
- Longer wavelength means higher frequency and lower energy.
- Longer wavelength means lower frequency and higher energy.
- Longer wavelength means higher frequency and higher energy.
- Longer wavelength means lower frequency and lower energy.
- There is no simple relationship because different photons travel at different speeds.
33) From shortest to longest wavelength, which of the following correctly orders the different categories of electromagnetic radiation?
- gamma rays, X rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, radio
- infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X rays, gamma rays, radio
- visible light, infrared, X rays, ultraviolet, gamma rays, radio
- gamma rays, X rays, visible light, ultraviolet, infrared, radio
- radio, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X rays, gamma rays
34) From lowest energy to highest energy, which of the following correctly orders the different categories of electromagnetic radiation?
- gamma rays, X rays, visible light, ultraviolet, infrared, radio
- visible light, infrared, X rays, ultraviolet, gamma rays, radio
- radio, X rays, visible light, ultraviolet, infrared, gamma rays
- infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X rays, gamma rays, radio
- radio, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X rays, gamma rays
35) Which of the following statements about X rays and radio waves is not true?
- X rays have higher energy than radio waves.
- X rays have higher frequency than radio waves.
- X rays and radio waves are both forms of light, or electromagnetic radiation.
- X rays have shorter wavelengths than radio waves.
- X rays travel through space faster than radio waves.
36) We can see each other in the classroom right now because we
- emit visible light.
- emit infrared light.
- emit thermal radiation.
- reflect infrared light.
- reflect visible light.
37) When an electron in an atom goes from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, the atom
- can absorb a photon of any frequency.
- emits a photon of a specific frequency.
- absorbs a photon of a specific frequency.
- can emit a photon of any frequency.
- absorbs several photons of a specific frequency.
38) If you heat a gas so that collisions are continually bumping electrons to higher energy levels, when the electrons fall back to lower energy levels the gas produces
- X rays.
- thermal radiation.
- radio waves.
- an absorption line spectrum.
- an emission line spectrum.
39) When white light passes through a cool cloud of gas, we see
- an absorption line spectrum.
- infrared light.
- an emission line spectrum.
- visible light.
- thermal radiation.
40) Spectra from neutral atoms compared with spectra from ionized atoms of the same element
- are slightly redshifted.
- have the same sets of spectral lines but different widths for those lines.
- are slightly blueshifted.
- have different sets of spectral lines.
- are the same.
41) Which of the following statements about thermal radiation is always true?
- A hot object emits more radio waves than a cool object.
- A hot object emits less total radiation than a cool object.
- A hot object emits more total radiation than a cool object.
- A hot object emits more X rays than a cool object.
- A hot object emits more total radiation per unit surface area than a cool object.
42) A gas heated to millions of degrees would emit
- mostly radio waves.
- mostly ultraviolet light.
- an equal amount of all wavelengths of light.
- mostly X rays.
- no light, because it is too hot.
43) Studying a spectrum from a star can tell us a lot. All of the following statements are true except one. Which one?
- The peak of the star's thermal emission tells us its temperature: Hotter stars peak at
shorter (bluer) wavelengths.
- We can look at Doppler shifts of spectral lines to determine the star's speed toward or
away from us.
- We can identify chemical elements present in the star by recognizing patterns of
spectral lines that correspond to particular chemicals.
- The total amount of light in the spectrum tells us the star's radius.
- Trick question; all of the above statements are true.
44) Use Newton's version of Kepler's third law: suppose a solar system has a star that is 9 times as massive as our Sun. If that solar system has a planet the same size as Earth orbiting at a distance of 1 AU, what is the orbital period of the planet?
- 1 year
- 3 years
- 1/9 of a year
- 9 years
- 1/3 of a year
45) Science is a human activity
- requiring large annual budgets
- done by professionals in national laboratories
- heavily dependent upon the latest computer technology
- accomplished, in its simplest form, by everyone every day
- all of the above
**Following is a schematic of the energy levels of an atom. Use this to answer questions 46-49:**
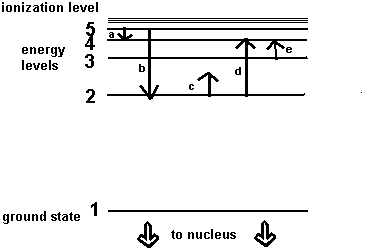 46) Which transition represents the smallest energy change?
46) Which transition represents the smallest energy change?
47) Which transition, as shown, is not possible?
48) Which of the two transitions resulting in an emission line represents the redder wavelength?
49) Which of the two transitions resulting in an absorption line represents the redder wavelength?
50) The spectrum of mercury gas looks like
- gold, which is also a heavy element
- platinum, since it has similar chemical properties
- ionized mercury
- no other element
- none of the above
51) Which of the following statements about scientific theories is not true?
- A theory must make predictions that can be checked by observation or experiment.
- A theory is a model designed to explain a number of observed facts.
- A theory can never be proved beyond all doubt; we can only hope to collect more and
more evidence that might support it.
- A theory cannot be taken seriously by scientists if it contradicts other theories
developed by scientists over the past several hundred years.
- If even a single new fact is discovered that contradicts what we expect according to a particular
theory, then the theory must be revised or discarded.
52) The Universe is made mostly of what?
- hydrogen and helium
- dark matter
- stars and galaxies and clouds of dust
- really nothing
- false energy
53) (3 points) How can the hydrogen atom that has only one electron generate multiple emission or absorption lines?
54) (5 points) We all know that it would take a much smaller force to push a gymnast off a ledge than a huge Sumo wrestler. Rearrange Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, to solve for a and discuss why a smaller force is needed to push the gymnast to obtain the same acceleration. Be sure to use the word inertia (correctly) in your explanation.
55) (5 points) How is an object orbiting the Sun in an eccentric orbit like a skater pulling in her arms to rotate faster?
56) (5 points) Examine the following two spectra:
 46) Which transition represents the smallest energy change?
46) Which transition represents the smallest energy change?
 46) Which transition represents the smallest energy change?
46) Which transition represents the smallest energy change?