Static Electricity
Select the best possible answer.
1. Two pith balls are both charged by contact with a plastic rod that has been rubbed by cat fur. What kind of charge will be on the pith balls?
a. Positive.
b. Negative.
c. No charge will appear on the pith balls.
d. One side of balls will be positive and the other side will be negative.
2. When a glass rod is rubbed by a nylon cloth, which of these two objects gains electrons?
a. The glass rod.
b. The nylon cloth.
c. None of these objects gain or lose electrons.
d. Each will gain some additional electrons.
3. Suppose the glass rod of the previous question is used to charge a metal-foil electroscope. What happens to the leaves of the metal-foil electroscope?
a. The leaves will be negatively charged, and they repel each other.
b. The leaves will be positively charges and they repel each other.
c. The leaves will be left uncharged and remain in their initial positions.
d. One leaf becomes positively charged and one negatively charged. They attract each other.
4. When you comb your hair with a plastic comb, what kind of charge does the comb acquire?
a. Positive.
b. Negative.
c. The comb will be left uncharged.
d. Parts of the comb will be negatively charged and some parts positively charged.
5. If you touch the metal ball of a charged electroscope with an uncharged glass rod held in your hand, what happens to the electroscope (i.e. what happens to the leaves of the electroscope)?
a. the electroscope becomes uncharged (i.e. leaves become uncharged and stay vertically)
b. the electroscope stays as its (i.e. leaves stay away from each other at the same angle as before)
c. the electroscope loses some of its charge to the rod (i.e. leaves stay at a smaller angle than before)
d. the electroscope draws more charge from the rod (i.e. leaves stay at a larger angle than before)
6. When a metal ball is charged by induction using a negatively charged plastic rod, what kind of charge does the ball acquire?
a. Positive charge.
b. Negative charge.
c. The ball cannot be charged by induction. Thus it remains neutral.
d. Different charges appear on the different sides of the ball.
7. What happens to the electric force between two electric charges if the distance between them is doubled?
a. The force decreases to 1/2 of its original value.
b. The force will not change and remains equal to its original value.
c. The force decreases to 1/4 of its original value.
d. The force increases to twice its original value.
8. If two charges are doubled in magnitude without changing the distance between them, what happened to the electric force that they exert on each other?
a. The force increases to 4 times its original value.
b. The force will not change and remains equal to its original value.
c. The force decreases to 1/4 of its original value.
d. The force increases to twice its original value.
9. Which force binds atoms and molecules together?
a. Gravitational force
b. Nuclear force
c. Electric force
d. Centripetal force
10. The fundamental force underlying all chemical reactions is:
a. Gravitational force
b. Nuclear force
c. Centripetal force
d. Electric force
11. A main difference between gravitational and electric forces is that electrical forces:
a. Attract.
b. Repel or attract.
c. Obey the inverse-square law.
d. Act only over shorter distances.
12. A balloon will stick to a wooden wall if the balloon is charged:
a. Negatively.
b. Positively.
c. Either way.
d. Neither way.
13. An electroscope is charged positively as shown by foil leaves that stand apart. As a negative charge is brought close to the electroscope, the leaves:
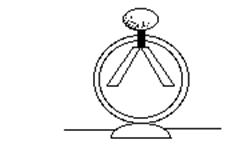
a. Fall closer together.
b. Spread apart further.
c. Do not move.
d. Touch each other and lose their charges.
14. Two charged particles exert an electrostatic force of 27 N on each other. What will be the magnitude of the force if the distance between them is increased to three times the original value?
a. 9 N.
b. 6.5 N.
c. 13.5 N.
d. 3 N.
15. Two charge particles apply a force 4 N to each other. What will be the magnitude of the force if the distance between them is decreased to one-half the original value?
a. 1 N.
b. 16 N.
c. 2 N.
d. 8 N.
16. Two identical steel balls mounted on wooden posts initially have charges of +12C and -4C. The balls are allowed to touch each other and then are separated again. What is the final charge on each ball?
a. +12C and +4C.
b. +8C and +8C.
c. +4C and +4C.
d. -4C and +12C.
17. Two positive charges of +4.45 x 10-6C are located at a distance of 10 cm from each other. What is the magnitude of the Coulomb force (electrostatic force) between them?
a. 17.8 N.
b. 1780 N.
c. 17800 N.
d. 178 N.